carbon2
-
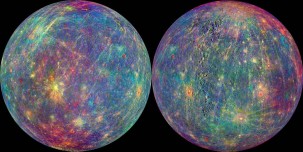
MESSENGER Data Reveal Evidence of Ancient Carbon-Rich Crust on Mercury
Mercury’s dark surface is revealing intriguing new clues about the formation of the solar system, including evidence announced today that the planet closest to the Sun may have formed in part from carbon, a key component of life.
-
From Copenhagen to Paris: Moving From Talk to Action on Climate Change
Globally, individual nations have volunteered greenhouse gas reduction targets in anticipation of the Paris meetings. Unlike Copenhagen, where calls for mandatory reductions and transfer payments to the developing world caused the collapse of any potential agreements, the world community seems more realistic as it approaches the Paris meetings.
-

Peat Fires Choking Southeast Asia Pose a New Threat to Global Climate
The Indonesian peat fires that have been choking cities across Southeast Asia with a yellow haze are creating more than a local menace—burning peat releases immense stores of CO2, contributing to global warming.
-

Seeing the Amazon’s Future Through the Fog
Scientists have developed a new approach to modeling the water and carbon cycles in the Amazon that could lead to better climate forecasts and improved water resource management.
-
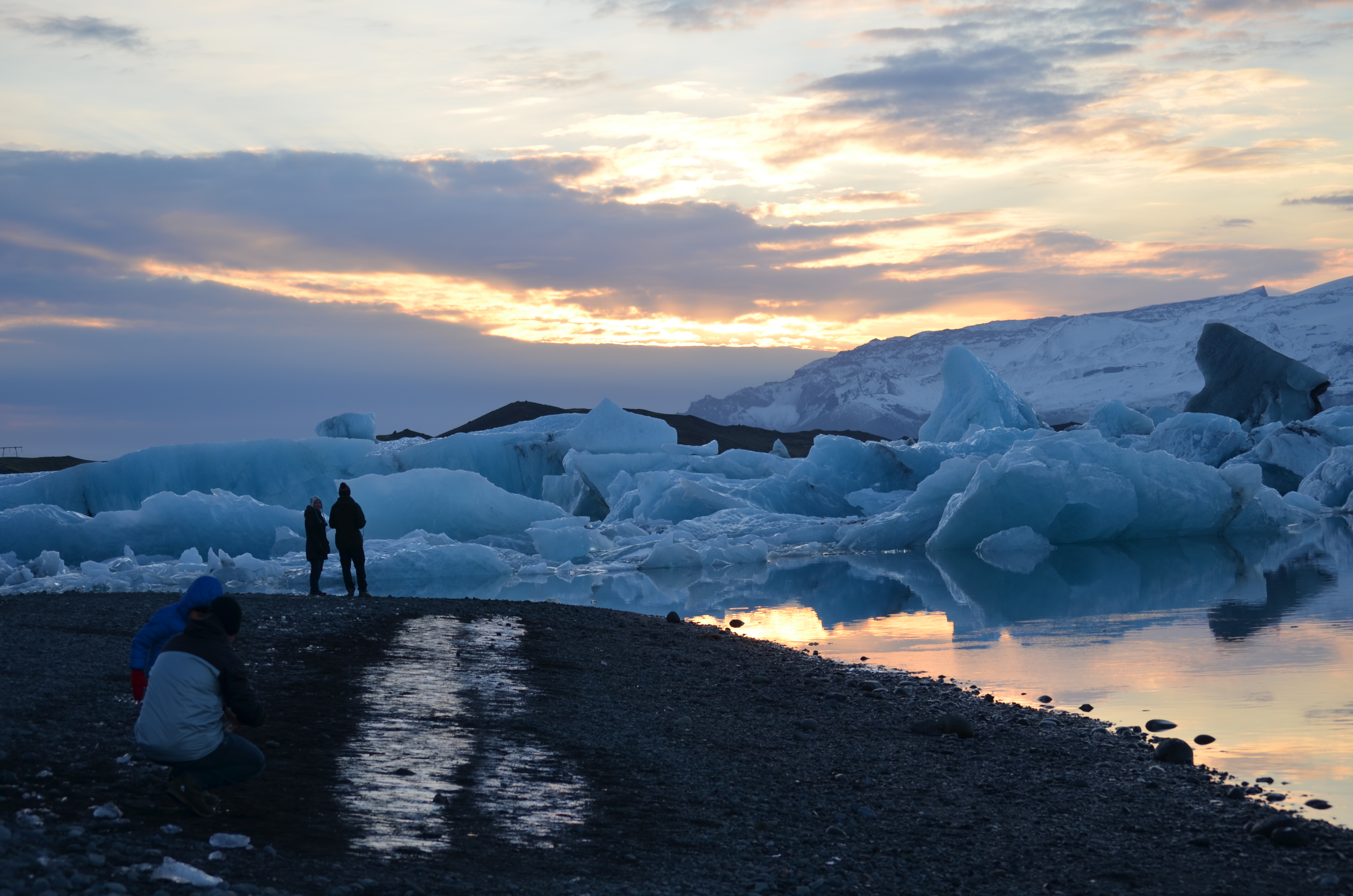

Photo Essay: Iceland at the Cutting Edge of Climate Change
Iceland has a complicated relationship with climate change. As in much of the far north, global warming is already exerting many effects here–arguably both good and bad. Yet the country contributes relatively little to the warming, since most of its energy comes from geothermal and hydro plants, which produce little carbon dioxide. Now, it is…
-

Columbia-PepsiCo Collaboration Creates Tool for Calculating Carbon Footprints
Researchers at the Earth Institute’s Lenfest Center for Sustainable Energy working in collaboration with PepsiCo, Inc. have developed new software that rapidly calculates the carbon footprints of thousands of products simultaneously.

By studying thousands of buildings and analyzing their electricity use, Columbia Climate School Dean Alexis Abramson has been able to uncover ways to significantly cut energy consumption and emissions. Watch the Video: “Engineering a Cooler Future Through Smarter Buildings“
