research38
-
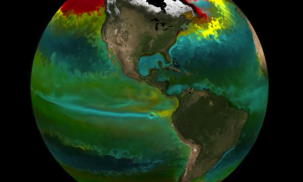
By 2100, Climate Change Could Alter Key Microbial Interactions in the Ocean
The warmer, more acidic waters caused by climate change influence the behavior of tiny marine organisms essential to ocean health.
-

Ice Sheets May Melt Rapidly in Response to Distant Volcanoes
A study of ancient eruptions shows modern ice sheets could be vulnerable.
-

Expedition Explores Undersea Rift off Greece
The Corinth rift is one of the most seismically active areas in Europe. Starting this month, researchers will drill into the rift to discover its past and future.
-

Ancient Humans Left Africa to Escape Drying Climate, Says Study
Ancient humans migrated out of Africa to escape a drying climate, says a new study—a finding that contradicts previous suggestions that ancient people were able to leave because a then-wet climate allowed them to cross the generally arid Horn of Africa and Middle East.
-

Study Bolsters Volcanic Theory of Ancient Extinction
A team of scientists has found new evidence to bolster the idea that the Permian Extinction, which occurred 252 million years ago, was caused by massive volcanic eruptions in what is now Siberia.
-

Seasonal Changes in Climate May Muddle Results of Malaria Interventions in Africa
A new climate study shows that some countries in sub-Saharan Africa may be underestimating the impact of their malaria control activities, while others may be underestimating their success.
-

Climate Change Could Spell Trouble for Europe’s Electrical Grid
Peak demand for electricity is expected to shift from winter to summer, and from Northern Europe to the South—changes that could strain the region’s infrastructure.
-

Climate May Quickly Drive Forest-Eating Beetles North, Says Study
Over the next few decades, global warming-related rises in winter temperatures could significantly extend the range of the southern pine beetle, one of the world’s most aggressive tree-killing insects, through much of the northern United States and southern Canada, says a new study.
-

New York’s Waterways Are Swimming in Plastic Microbeads
Plastic microbeads, common in soap, toothpaste and other consumer products, are flooding waters. A team from Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory is doing the first large-scale assessment of their impact on New York’s waterways.

By studying thousands of buildings and analyzing their electricity use, Columbia Climate School Dean Alexis Abramson has been able to uncover ways to significantly cut energy consumption and emissions. Watch the Video: “Engineering a Cooler Future Through Smarter Buildings“
